Introduction
SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer Testing uses target region capture combined with high-throughput sequencing technology to detect 90 germline genes and assess the risk of 25 types of cancer. It mainly covers the exons and adjacent +20bp intron regions of hereditary tumor-related genes. And provide families with a comprehensive genetic cancer risk assessment.
What clinical challenges are targeted by SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer testing
Hereditary cancer is caused by germline mutations which is derived from germ cells and passed down from generation to generation, accounting for approximately 5-10% of all cancers, it has some features: such as familial clustering, early-onset, usually occuring before age 45, multiple primary rare tumors.
A hereditary cancer syndrome is a genetic predisposition to certain types of cancer.For healthy people, genetic gene testing can assess cancer risk and take timely intervention and management measures to reduce the risk of future tumors. For cancer patients, it can help them discover the risk of a second tumor and evaluate the efficacy of PARP inhibitors.The NCCN guidelines also recommend assessing the risk of hereditary tumors based on genetic testing results.
Although the detection of hereditary tumors is very important, there are currently three major difficulties.
First, there are no hotspot mutations in germline genes related to hereditary tumors. Especially in Latin America, Asia and some weekly populations, the mutations of BRCA1/2 are random. At the same time, the entire exon region of BRCA1 /2 is very long, which means that it is easy to miss the detection using conventional methods.
Second, the occurrence of hereditary gender tumors is not caused by a single gene, but usually by multiple genes. At the same time, a single gene mutation can also lead to a variety of hereditary tumors, which means that if only a few gene mutations or a single cancer are detected, it is far from enough to fully assess the risk of hereditary tumors.
Third, there are many types of mutations in hereditary tumors, including SNV, indel, CNV and large fragment mutations. If traditional Sanger sequencing, qPCR methods or MLPA are used, it is not possible to detect all types of mutations covering BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes at one time. In contrast, high-throughput sequencing technology is more efficient and fast and can detect mutations in all exons and adjacent upstream and downstream regions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes at one time. It can also discover some unknown mutations and stand out with a higher cost-effectiveness.
Applicable Clinical Scenarios
• Cancer patients
• people with cancer family history
Important features of SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer testing
Gene Numbers | 90 genes ( it can be expanded to 171 genes) |
Cancer types | 25 hereditary cancer types |
Detection method | NGS (Target region capture) |
Detection platform | DNBSEQ-G99, DNBSEQ-G400 |
Detection scope | SNV, indel (whole exons)and ±20bp introns, CNV |
Sample type | Blood/saliva |
Sequencing depth | Sequence depth of BRCA1/2> 200X Sequence depth of whole panel>150x Female panel (85 genes 24 cancer types) Male panel (90 genes 23 cancer types) |
Detection significance | Cancer risk assessment for healthy people Assess the risk of developing the second tumor for cancer patients |
Sample type | Peripheral blood or saliva |
SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer testing service process
STEP 1
Physician orders test
STEP 2
Sample collected

STEP 3
Sample shipped to us and analyzed

STEP 4
Results sent to physician
STEP 1
Physician orders test

STEP 2
Sample collected

STEP 3
Sample shipped to us and analyzed

STEP 4
Results sent to physician
Why Choose SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer testing
- Comprehensive
Whole-exome plus flanking intronic regions covered for all genes tested; one single assay that detects point mutations, deletions, insertions, duplications, rearrangements.
Providing risk assessment and risk arrangement is help to closed-loop management.
- Accurate
Compared with the library construction method based on multiplex PCR amplification, the hybridization capture technology can more accurately and uniformly detect SNV, indel and CNV, and reduce the false positive rate.
Professional database ensures up-to-date analysis and interpretation.
- Convenient
Test from blood or saliva, DNA is also accepted
Note: this test is considered a screening test, not a diagnostic test. Before making any treatment decisions, all patients should discuss their results with their healthcare provider, who can recommend confirmatory, diagnostic testing where appropriate. This testing service has not been cleared or approved by the US FDA and is not available in the USA.
Localization solution of SENTIS™ Hereditary Cancer testing
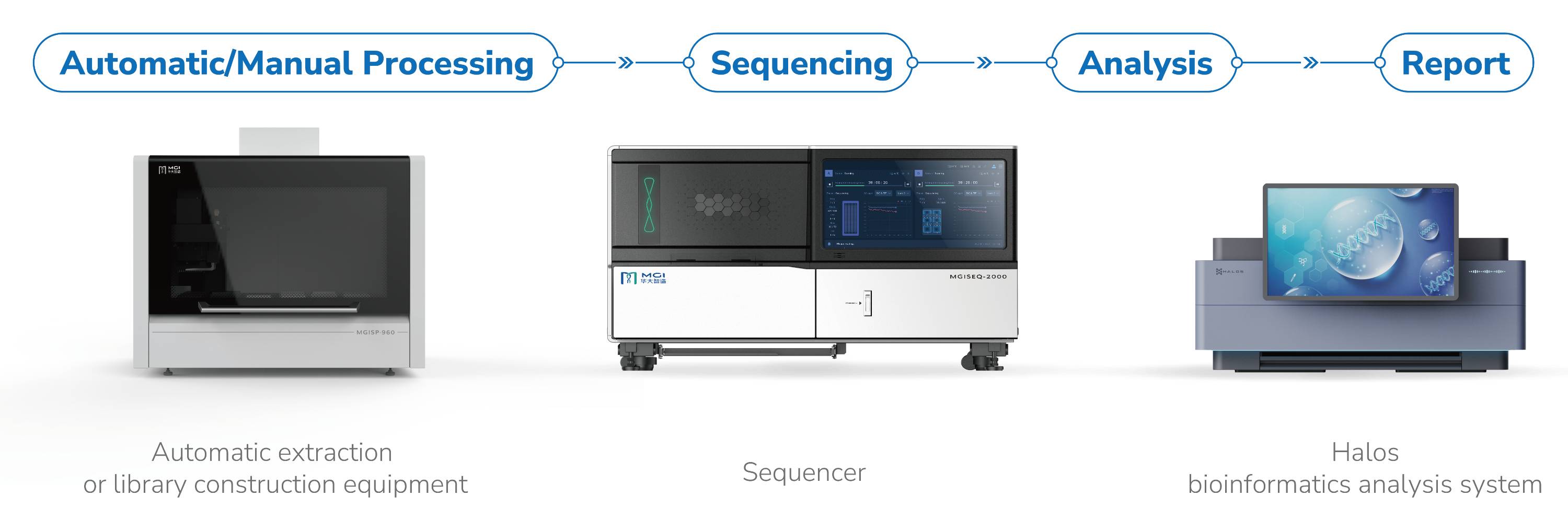

Automation equipment | Sequencer | Maximum samples/ Flow cell | Sequencing time | Bioinformatics analysis |
Manual | DNBSEQ-G400 | 64 samples/ 1 FCL | 35h | HALOS (Premium version) |
32 samples/ 1 FCS | 22h | |||
DNBSEQ-G99 | 10 samples/ 1 FCL | 9h |
- Enhanced Productivity
Rapid turnaround with going from DNA to report in approximately based on DNBSEQ-G99.
- User-Friendly Analysis and Reporting
After the task is created in Halos, it is unattended and directly waits for the analysis results.
- Flexible throughput
Target region sequencing of 1032/64 samples can be performed at a time depending on different sequencing platforms.
- Accurate detection
Patented DNB nanoball (DNB) library construction technology and Combinatorial Probe-Anchor Synthesis sequencing technology.
- Safe and reliable
Offline operation, Localized web design and data storage, the account hierarchical management.



